如何添加聊天历史
在许多问答应用中,我们希望允许用户进行来回对话,这意味着应用需要某种形式的“记忆”来记录过去的问题和答案,以及将这些信息纳入当前思考的逻辑。
在本指南中,我们专注于添加纳入历史消息的逻辑。
这在很大程度上是对话式RAG教程的简化版本。
我们将介绍两种方法:
对于外部知识源,我们将使用Lilian Weng的LLM驱动的自主代理博客文章,该文章来自RAG教程。
设置
依赖
在本次演示中,我们将使用OpenAI嵌入和Chroma向量存储,但这里展示的所有内容都适用于任何嵌入模型、向量存储或检索器。
我们将使用以下第三方库:
%%capture --no-stderr
%pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain langchain-community langchain-chroma beautifulsoup4
我们需要设置环境变量 OPENAI_API_KEY,可以直接设置或从 .env 文件中加载,如下所示:
import getpass
import os
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
# import dotenv
# dotenv.load_dotenv()
LangSmith
使用 LangChain 构建的许多应用程序将包含多个步骤和多次调用大型语言模型(LLM)。随着这些应用程序变得越来越复杂,能够检查链或代理内部发生的具体情况变得至关�重要。最好的方法是使用 LangSmith。
请注意,LangSmith 不是必需的,但它是有帮助的。如果您确实想使用 LangSmith,在您在上述链接注册后,请确保设置您的环境变量以开始记录跟踪:
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
if not os.environ.get("LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"):
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
链
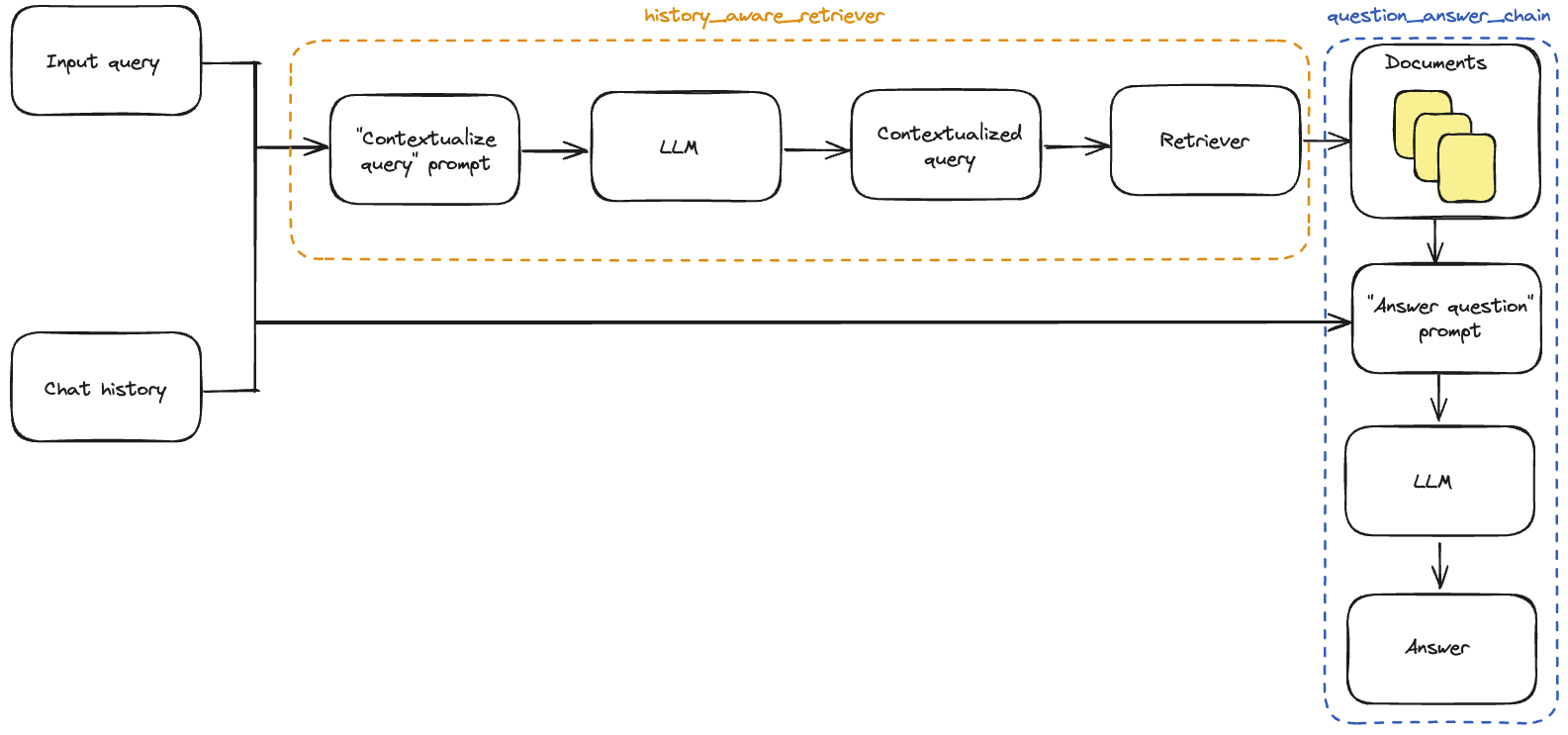
在对话式 RAG 应用程序中,发给检索器的查询应受到对话上下文的影响。LangChain 提供了一个 create_history_aware_retriever 构造函数来简化这一过程。它构建了一个接受 input 和 chat_history 作为输入的链,并具有与检索器相同的输出模式。create_history_aware_retriever 需要以下输入:
- 大型语言模型(LLM);
- 检索器;
- 提示词。
首先我们获取这些对象:
大型语言模型
我们可以使用任何支持的聊天模型:
- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Azure
- Cohere
- NVIDIA
- FireworksAI
- Groq
- MistralAI
- TogetherAI
pip install -qU langchain-openai
import getpass
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
pip install -qU langchain-anthropic
import getpass
import os
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
llm = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620")
pip install -qU langchain-openai
import getpass
import os
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(
azure_endpoint=os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"],
azure_deployment=os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME"],
openai_api_version=os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION"],
)
pip install -qU langchain-google-vertexai
import getpass
import os
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_google_vertexai import ChatVertexAI
llm = ChatVertexAI(model="gemini-1.5-flash")
pip install -qU langchain-cohere
import getpass
import os
os.environ["COHERE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_cohere import ChatCohere
llm = ChatCohere(model="command-r-plus")
pip install -qU langchain-nvidia-ai-endpoints
import getpass
import os
os.environ["NVIDIA_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain import ChatNVIDIA
llm = ChatNVIDIA(model="meta/llama3-70b-instruct")
pip install -qU langchain-fireworks
import getpass
import os
os.environ["FIREWORKS_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_fireworks import ChatFireworks
llm = ChatFireworks(model="accounts/fireworks/models/llama-v3p1-70b-instruct")
pip install -qU langchain-groq
import getpass
import os
os.environ["GROQ_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
llm = ChatGroq(model="llama3-8b-8192")
pip install -qU langchain-mistralai
import getpass
import os
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_mistralai import ChatMistralAI
llm = ChatMistralAI(model="mistral-large-latest")
pip install -qU langchain-openai
import getpass
import os
os.environ["TOGETHER_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
base_url="https://api.together.xyz/v1",
api_key=os.environ["TOGETHER_API_KEY"],
model="mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1",
)
检索器
对于检索器,我们将使用 WebBaseLoader 来加载网页内容。在这里,我们实例化一个 Chroma 向量存储,然后使用它的 .as_retriever 方法构建一个可以纳入 LCEL 链的检索器。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "create_retrieval_chain", "source": "langchain.chains", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.retrieval.create_retrieval_chain.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "create_stuff_documents_chain", "source": "langchain.chains.combine_documents", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.combine_documents.stuff.create_stuff_documents_chain.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "Chroma", "source": "langchain_chroma", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/chroma/vectorstores/langchain_chroma.vectorstores.Chroma.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "WebBaseLoader", "source": "langchain_community.document_loaders", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/community/document_loaders/langchain_community.document_loaders.web_base.WebBaseLoader.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "StrOutputParser", "source": "langchain_core.output_parsers", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/output_parsers/langchain_core.output_parsers.string.StrOutputParser.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "ChatPromptTemplate", "source": "langchain_core.prompts", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/prompts/langchain_core.prompts.chat.ChatPromptTemplate.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RunnablePassthrough", "source": "langchain_core.runnables", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/runnables/langchain_core.runnables.passthrough.RunnablePassthrough.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "OpenAIEmbeddings", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/embeddings/langchain_openai.embeddings.base.OpenAIEmbeddings.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter", "source": "langchain_text_splitters", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/text_splitters/character/langchain_text_splitters.character.RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
import bs4
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",),
bs_kwargs=dict(
parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(
class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header")
)
),
)
docs = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings())
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
提示词
我们将使用一个包含名为 "chat_history" 的 MessagesPlaceholder 变量的提示词。这允许我们通过 "chat_history" 输入键将消息列表传递给提示词,这些消息将在系统消息之后和包含最新问题的人类消息之前插入。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "create_history_aware_retriever", "source": "langchain.chains", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.history_aware_retriever.create_history_aware_retriever.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "MessagesPlaceholder", "source": "langchain_core.prompts", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/prompts/langchain_core.prompts.chat.MessagesPlaceholder.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
from langchain.chains import create_history_aware_retriever
from langchain_core.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder
contextualize_q_system_prompt = (
"Given a chat history and the latest user question "
"which might reference context in the chat history, "
"formulate a standalone question which can be understood "
"without the chat history. Do NOT answer the question, "
"just reformulate it if needed and otherwise return it as is."
)
contextualize_q_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", contextualize_q_system_prompt),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
组装链
然后我们可以实例化历史感知检索器:
history_aware_retriever = create_history_aware_retriever(
llm, retriever, contextualize_q_prompt
)
该链在我们的检索器之前添加了输入查询的重述,以便检索包含对话上下文。
现在我们可以构建完整的问答链。
如RAG教程所示,我们将使用create_stuff_documents_chain生成一个question_answer_chain,输入键为context、chat_history和input——它接受检索到的上下文以及对话历史和查询以生成答案。
我们使用create_retrieval_chain构建最终的rag_chain。该链依次应用history_aware_retriever和question_answer_chain,保留中间输出,例如检索到的上下文,以便于使用。它的输入键为input和chat_history,并在输出中包含input、chat_history、context和answer。
system_prompt = (
"You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. "
"Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer "
"the question. If you don't know the answer, say that you "
"don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the "
"answer concise."
"\n\n"
"{context}"
)
qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_prompt),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
question_answer_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, qa_prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(history_aware_retriever, question_answer_chain)
添加聊天历史
为了管理聊天历史,我们需要:
- 一个用于存储聊天历史的对象;
- 一个包装我们的链并管理聊天历史更新的对象。
为此,我们将使用BaseChatMessageHistory和RunnableWithMessageHistory。后者是一个LCEL链和BaseChatMessageHistory的包装器,处理将聊天历史注入输入并在每次调用后更新它。
有关如何将这些类结合使用以创建有状态对话链的详细指南,请查看如何添加消息历史(记忆)的LCEL使用手册。
下面,我们实现第二种选项的简单示例,其中聊天历史存储在一个简单的字典中。LangChain与Redis和其他技术管理内存集成,以提供更强大的持久性。
RunnableWithMessageHistory的实例为您管理聊天历史。它们接受一个配置,其中包含一个键(默认为`
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "ChatMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_community.chat_message_histories", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/chat_history/langchain_core.chat_history.ChatMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "BaseChatMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_core.chat_history", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/chat_history/langchain_core.chat_history.BaseChatMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RunnableWithMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_core.runnables.history", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/runnables/langchain_core.runnables.history.RunnableWithMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.chat_history import BaseChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str) -> BaseChatMessageHistory:
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
conversational_rag_chain = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
rag_chain,
get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history",
output_messages_key="answer",
)
conversational_rag_chain.invoke(
{"input": "What is Task Decomposition?"},
config={
"configurable": {"session_id": "abc123"}
}, # constructs a key "abc123" in `store`.
)["answer"]
'Task decomposition involves breaking down a complex task into smaller and simpler steps to make it more manageable and easier to accomplish. This process can be done using techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts to guide the model in breaking down tasks effectively. Task decomposition can be facilitated by providing simple prompts to a language model, task-specific instructions, or human inputs.'
conversational_rag_chain.invoke(
{"input": "What are common ways of doing it?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "abc123"}},
)["answer"]
'Task decomposition can be achieved through various methods, including using techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts to guide the model in breaking down tasks effectively. Common ways of task decomposition include providing simple prompts to a language model, task-specific instructions, or human inputs to break down complex tasks into smaller and more manageable steps. Additionally, task decomposition can involve utilizing resources like internet access for information gathering, long-term memory management, and GPT-3.5 powered agents for delegation of simple tasks.'
可以在 store 字典中检查聊天历史:
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "AIMessage", "source": "langchain_core.messages", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/messages/langchain_core.messages.ai.AIMessage.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage
for message in store["abc123"].messages:
if isinstance(message, AIMessage):
prefix = "AI"
else:
prefix = "User"
print(f"{prefix}: {message.content}\n")
User: What is Task Decomposition?
AI: Task decomposition involves breaking down a complex task into smaller and simpler steps to make it more manageable and easier to accomplish. This process can be done using techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts to guide the model in breaking down tasks effectively. Task decomposition can be facilitated by providing simple prompts to a language model, task-specific instructions, or human inputs.
User: What are common ways of doing it?
AI: Task decomposition can be achieved through various methods, including using techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts to guide the model in breaking down tasks effectively. Common ways of task decomposition include providing simple prompts to a language model, task-specific instructions, or human inputs to break down complex tasks into smaller and more manageable steps. Additionally, task decomposition can involve utilizing resources like internet access for information gathering, long-term memory management, and GPT-3.5 powered agents for delegation of simple tasks.
将其结合起来
为了方便,我们将所有必要步骤结合在一个代码单元中:
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "create_history_aware_retriever", "source": "langchain.chains", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.history_aware_retriever.create_history_aware_retriever.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "create_retrieval_chain", "source": "langchain.chains", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.retrieval.create_retrieval_chain.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "create_stuff_documents_chain", "source": "langchain.chains.combine_documents", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/langchain/chains/langchain.chains.combine_documents.stuff.create_stuff_documents_chain.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "Chroma", "source": "langchain_chroma", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/chroma/vectorstores/langchain_chroma.vectorstores.Chroma.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "ChatMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_community.chat_message_histories", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/chat_history/langchain_core.chat_history.ChatMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "WebBaseLoader", "source": "langchain_community.document_loaders", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/community/document_loaders/langchain_community.document_loaders.web_base.WebBaseLoader.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "BaseChatMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_core.chat_history", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/chat_history/langchain_core.chat_history.BaseChatMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "ChatPromptTemplate", "source": "langchain_core.prompts", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/prompts/langchain_core.prompts.chat.ChatPromptTemplate.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "MessagesPlaceholder", "source": "langchain_core.prompts", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/prompts/langchain_core.prompts.chat.MessagesPlaceholder.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RunnableWithMessageHistory", "source": "langchain_core.runnables.history", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/runnables/langchain_core.runnables.history.RunnableWithMessageHistory.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "ChatOpenAI", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/chat_models/langchain_openai.chat_models.base.ChatOpenAI.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "OpenAIEmbeddings", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/embeddings/langchain_openai.embeddings.base.OpenAIEmbeddings.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter", "source": "langchain_text_splitters", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/text_splitters/character/langchain_text_splitters.character.RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
import bs4
from langchain.chains import create_history_aware_retriever, create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.chat_history import BaseChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
### Construct retriever ###
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",),
bs_kwargs=dict(
parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(
class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header")
)
),
)
docs = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings())
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
### Contextualize question ###
contextualize_q_system_prompt = (
"Given a chat history and the latest user question "
"which might reference context in the chat history, "
"formulate a standalone question which can be understood "
"without the chat history. Do NOT answer the question, "
"just reformulate it if needed and otherwise return it as is."
)
contextualize_q_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", contextualize_q_system_prompt),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
history_aware_retriever = create_history_aware_retriever(
llm, retriever, contextualize_q_prompt
)
### Answer question ###
system_prompt = (
"You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. "
"Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer "
"the question. If you don't know the answer, say that you "
"don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the "
"answer concise."
"\n\n"
"{context}"
)
qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_prompt),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
question_answer_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, qa_prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(history_aware_retriever, question_answer_chain)
### Statefully manage chat history ###
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str) -> BaseChatMessageHistory:
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
conversational_rag_chain = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
rag_chain,
get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history",
output_messages_key="answer",
)
conversational_rag_chain.invoke(
{"input": "What is Task Decomposition?"},
config={
"configurable": {"session_id": "abc123"}
}, # constructs a key "abc123" in `store`.
)["answer"]
'Task decomposition involves breaking down a complex task into smaller and simpler steps to make it more manageable. Techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tree of Thoughts help in decomposing hard tasks into multiple manageable tasks by instructing models to think step by step and explore multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. Task decomposition can be achieved through various methods such as using prompting techniques, task-specific instructions, or human inputs.'
conversational_rag_chain.invoke(
{"input": "What are common ways of doing it?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "abc123"}},
)["answer"]
'Task decomposition can be done in common ways such as using prompting techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts, which instruct models to think step by step and explore multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. Another way is to provide task-specific instructions, such as asking to "Write a story outline" for writing a novel, to guide the decomposition process. Additionally, task decomposition can also involve human inputs to break down complex tasks into smaller and simpler steps.'
代理
代理利用大型语言模型的推理能力在执行过程中做出决策。使用代理可以将一些检索过程的自由裁量权转移出去。尽管它们的行为比链式结构更不可预测,但在这种情况下它们提供了一些优势:
- 代理直接生成检索器的输入,而不一定需要我们像上面那样明确构建上下文;
- 代理可以为查询执行多个检索步骤,或者完全不执行检索步骤(例如,响应用户的通用问候时)。
检索工具
代理可以访问“工具”并管理其执行。在这种情况下,我们将把检索器转换为一个 LangChain 工具,以供代理使用:
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "create_retriever_tool", "source": "langchain.tools.retriever", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/tools/langchain_core.tools.retriever.create_retriever_tool.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
tool = create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"blog_post_retriever",
"Searches and returns excerpts from the Autonomous Agents blog post.",
)
tools = [tool]
代理构造�器
现在我们已经定义了工具和大型语言模型,我们可以创建代理。我们将使用 LangGraph 来构建代理。 目前我们正在使用高级接口来构建代理,但 LangGraph 的一个优点是这个高级接口背后有一个低级的、高度可控的 API,以便您想要修改代理逻辑时使用。
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
agent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, tools)
我们现在可以试一试。请注意,到目前为止它是无状态的(我们仍然需要添加内存)。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "HumanMessage", "source": "langchain_core.messages", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/messages/langchain_core.messages.human.HumanMessage.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
query = "What is Task Decomposition?"
for s in agent_executor.stream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]},
):
print(s)
print("----")
Error in LangChainTracer.on_tool_end callback: TracerException("Found chain run at ID 5cd28d13-88dd-4eac-a465-3770ac27eff6, but expected {'tool'} run.")
``````output
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_TbhPPPN05GKi36HLeaN4QM90', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"Task Decomposition"}', 'name': 'blog_post_retriever'}, 'type': 'function'}]}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 19, 'prompt_tokens': 68, 'total_tokens': 87}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-2e60d910-879a-4a2a-b1e9-6a6c5c7d7ebc-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'blog_post_retriever', 'args': {'query': 'Task Decomposition'}, 'id': 'call_TbhPPPN05GKi36HLeaN4QM90'}])]}}
----
{'tools': {'messages': [ToolMessage(content='Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nFig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.', name='blog_post_retriever', tool_call_id='call_TbhPPPN05GKi36HLeaN4QM90')]}}
----
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='Task decomposition is a technique used to break down complex tasks into smaller and simpler steps. This approach helps in transforming big tasks into multiple manageable tasks, making it easier for autonomous agents to handle and interpret the thinking process. One common method for task decomposition is the Chain of Thought (CoT) technique, where models are instructed to "think step by step" to decompose hard tasks. Another extension of CoT is the Tree of Thoughts, which explores multiple reasoning possibilities at each step by creating a tree structure of multiple thoughts per step. Task decomposition can be facilitated through various methods such as using simple prompts, task-specific instructions, or human inputs.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 130, 'prompt_tokens': 636, 'total_tokens': 766}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-3ef17638-65df-4030-a7fe-795e6da91c69-0')]}}
----
LangGraph 内置了持久化功能,因此我们不需要使用 ChatMessageHistory!相反,我们可以直接将检查点传递给我们的 LangGraph 代理。
通过在配置字典中为对话线程指定一个键,可以管理不同的对话,如下所示。
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
agent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, tools, checkpointer=memory)
这就是构建对话式 RAG 代理所需的一切。
让我们观察它的行为。请注意,如果我们输入一个不需要检索步骤的查询,代理不会执行检索:
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "abc123"}}
for s in agent_executor.stream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content="Hi! I'm bob")]}, config=config
):
print(s)
print("----")
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='Hello Bob! How can I assist you today?', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 11, 'prompt_tokens': 67, 'total_tokens': 78}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-1cd17562-18aa-4839-b41b-403b17a0fc20-0')]}}
----
此外,如果我们输入一个确实需要检索步骤的查询,代理会生成工具的输入:
query = "What is Task Decomposition?"
for s in agent_executor.stream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}, config=config
):
print(s)
print("----")
Error in LangChainTracer.on_tool_end callback: TracerException("Found chain run at ID c54381c0-c5d9-495a-91a0-aca4ae755663, but expected {'tool'} run.")
``````output
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_rg7zKTE5e0ICxVSslJ1u9LMg', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"Task Decomposition"}', 'name': 'blog_post_retriever'}, 'type': 'function'}]}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 19, 'prompt_tokens': 91, 'total_tokens': 110}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-122bf097-7ff1-49aa-b430-e362b51354ad-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'blog_post_retriever', 'args': {'query': 'Task Decomposition'}, 'id': 'call_rg7zKTE5e0ICxVSslJ1u9LMg'}])]}}
----
{'tools': {'messages': [ToolMessage(content='Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nFig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.', name='blog_post_retriever', tool_call_id='call_rg7zKTE5e0ICxVSslJ1u9LMg')]}}
----
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='Task decomposition is a technique used to break down complex tasks into smaller and simpler steps. This approach helps in managing and solving intricate problems by dividing them into more manageable components. By decomposing tasks, agents or models can better understand the steps involved and plan their actions accordingly. Techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tree of Thoughts are examples of methods that enhance model performance on complex tasks by breaking them down into smaller steps.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 87, 'prompt_tokens': 659, 'total_tokens': 746}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-b9166386-83e5-4b82-9a4b-590e5fa76671-0')]}}
----
在上面,代理没有逐字插入我们的查询到工具中,而是剔除了“什么”和“是”等不必要的词。
同样的原则允许代理在必要时使用对话的上下文:
query = "What according to the blog post are common ways of doing it? redo the search"
for s in agent_executor.stream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}, config=config
):
print(s)
print("----")
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_6kbxTU5CDWLmF9mrvR7bWSkI', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"Common ways of task decomposition"}', 'name': 'blog_post_retriever'}, 'type': 'function'}]}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 21, 'prompt_tokens': 769, 'total_tokens': 790}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-2d2c8327-35cd-484a-b8fd-52436657c2d8-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'blog_post_retriever', 'args': {'query': 'Common ways of task decomposition'}, 'id': 'call_6kbxTU5CDWLmF9mrvR7bWSkI'}])]}}
----
``````output
Error in LangChainTracer.on_tool_end callback: TracerException("Found chain run at ID 29553415-e0f4-41a9-8921-ba489e377f68, but expected {'tool'} run.")
``````output
{'tools': {'messages': [ToolMessage(content='Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nFig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.\n\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.', name='blog_post_retriever', tool_call_id='call_6kbxTU5CDWLmF9mrvR7bWSkI')]}}
----
{'agent': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='Common ways of task decomposition include:\n1. Using LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ" or "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?"\n2. Using task-specific instructions, for example, "Write a story outline" for writing a novel.\n3. Involving human inputs in the task decomposition process.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 67, 'prompt_tokens': 1339, 'total_tokens': 1406}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-9ad14cde-ca75-4238-a868-f865e0fc50dd-0')]}}
----
请注意,代理能够推断出我们查询中的“它”指的是“任务分解”,并因此生成了一个合理的搜索查询——在这种情况下是“任务分解的常见方法”。
整合起来
为了方便,我们将所有必要步骤整合在一个代码单元中:
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "create_retriever_tool", "source": "langchain.tools.retriever", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/tools/langchain_core.tools.retriever.create_retriever_tool.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "Chroma", "source": "langchain_chroma", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/chroma/vectorstores/langchain_chroma.vectorstores.Chroma.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "WebBaseLoader", "source": "langchain_community.document_loaders", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/community/document_loaders/langchain_community.document_loaders.web_base.WebBaseLoader.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "ChatOpenAI", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/chat_models/langchain_openai.chat_models.base.ChatOpenAI.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "OpenAIEmbeddings", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/embeddings/langchain_openai.embeddings.base.OpenAIEmbeddings.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}, {"imported": "RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter", "source": "langchain_text_splitters", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/text_splitters/character/langchain_text_splitters.character.RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.html", "title": "How to add chat history"}]-->
import bs4
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
### Construct retriever ###
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",),
bs_kwargs=dict(
parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(
class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header")
)
),
)
docs = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings())
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
### Build retriever tool ###
tool = create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"blog_post_retriever",
"Searches and returns excerpts from the Autonomous Agents blog post.",
)
tools = [tool]
agent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, tools, checkpointer=memory)
下一步
我们已经涵盖了构建基本对话式问答应用程序的步骤:
- 我们使用链构建了一个可预测的应用程序,为每个用户输入生成搜索查询;
- 我们使用代理构建了一个“决定”何时以及如何生成搜索查询的应用程序。
要探索不同类型的检索器和检索策略,请访问检索器部分的使用手册。
有关LangChain对话记忆抽象的详细讲解,请访问如何添加消息历史(记忆)的LCEL页面。
要了解更多关于代理的信息,请前往代理模块。