如何构建知识图谱
在本指南中,我们将介绍基于非结构化文本构建知识图谱的基本方�法。构建的图谱可以作为RAG应用中的知识库使用。
⚠️ 安全提示 ⚠️
构建知识图谱需要对数据库执行写入访问。这存在固有的风险。在导入数据之前,请确保验证和确认数据的准确性。有关一般安全最佳实践的更多信息,请查看这里。
架构
从文本构建知识图谱的高层步骤如下:
- 从文本中提取结构化信息:模型用于从文本中提取结构化图信息。
- 存储到图数据库:将提取的结构化图信息存储到图数据库中,以支持下游RAG应用。
设置
首先,获取所需的包并设置环境变量。 在这个例子中,我们将使用Neo4j图形数据库。
%pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain langchain-community langchain-openai langchain-experimental neo4j
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
在本指南中,我们默认使用OpenAI模型。
import getpass
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
# Uncomment the below to use LangSmith. Not required.
# os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
# os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
········
接下来,我们需要定义Neo4j凭据和连接。 请按照这些安装步骤设置Neo4j数据库。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "Neo4jGraph", "source": "langchain_community.graphs", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/community/graphs/langchain_community.graphs.neo4j_graph.Neo4jGraph.html", "title": "How to construct knowledge graphs"}]-->
import os
from langchain_community.graphs import Neo4jGraph
os.environ["NEO4J_URI"] = "bolt://localhost:7687"
os.environ["NEO4J_USERNAME"] = "neo4j"
os.environ["NEO4J_PASSWORD"] = "password"
graph = Neo4jGraph()
LLM图形转换器
从文本中提取图形数据可以将非结构化信息转化为结构化格式,从而促进更深入的洞察和更高效地导航复杂的关系和模式。LLMGraphTransformer通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)解析和分类实体及其关系,将文本文档转换为结构化图形文档。LLM模型的选择显著影响输出,因为它决定了提取的图形数据的准确性和细微差别。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "LLMGraphTransformer", "source": "langchain_experimental.graph_transformers", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/experimental/graph_transformers/langchain_experimental.graph_transformers.llm.LLMGraphTransformer.html", "title": "How to construct knowledge graphs"}, {"imported": "ChatOpenAI", "source": "langchain_openai", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/openai/chat_models/langchain_openai.chat_models.base.ChatOpenAI.html", "title": "How to construct knowledge graphs"}]-->
import os
from langchain_experimental.graph_transformers import LLMGraphTransformer
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model_name="gpt-4-turbo")
llm_transformer = LLMGraphTransformer(llm=llm)
现在我们可以传入示例文本并检查结果。
<!--IMPORTS:[{"imported": "Document", "source": "langchain_core.documents", "docs": "https://python.langchain.com/api_reference/core/documents/langchain_core.documents.base.Document.html", "title": "How to construct knowledge graphs"}]-->
from langchain_core.documents import Document
text = """
Marie Curie, born in 1867, was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity.
She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the first person to win a Nobel Prize twice, and the only person to win a Nobel Prize in two scientific fields.
Her husband, Pierre Curie, was a co-winner of her first Nobel Prize, making them the first-ever married couple to win the Nobel Prize and launching the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes.
She was, in 1906, the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris.
"""
documents = [Document(page_content=text)]
graph_documents = llm_transformer.convert_to_graph_documents(documents)
print(f"Nodes:{graph_documents[0].nodes}")
print(f"Relationships:{graph_documents[0].relationships}")
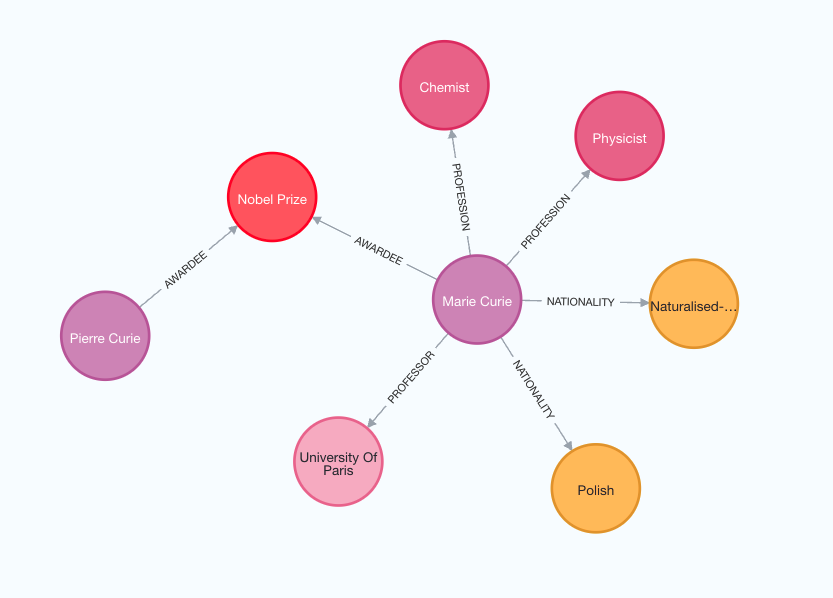
Nodes:[Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization')]
Relationships:[Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), type='MARRIED'), Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization'), type='PROFESSOR')]
查看以下图像以更好地理解生成的知识图谱的结构。
请注意,图形构建过程是非确定性的,因为我们使用的是大型语言模型(LLM)。因此,您可能在每次执行时获得略有不同的结果。
此外,您可以根据需求灵活定义特定类型的节点和关系进行提取。
llm_transformer_filtered = LLMGraphTransformer(
llm=llm,
allowed_nodes=["Person", "Country", "Organization"],
allowed_relationships=["NATIONALITY", "LOCATED_IN", "WORKED_AT", "SPOUSE"],
)
graph_documents_filtered = llm_transformer_filtered.convert_to_graph_documents(
documents
)
print(f"Nodes:{graph_documents_filtered[0].nodes}")
print(f"Relationships:{graph_documents_filtered[0].relationships}")
Nodes:[Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization')]
Relationships:[Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), type='SPOUSE'), Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization'), type='WORKED_AT')]
为了更好地理解生成的图形,我们可以再次对其进行可视化。

node_properties 参数使得可以提取节点属性,从而创建更详细的图形。
当设置为 True 时,LLM 会自主识别并提取相关的节点属性。
相反,如果 node_properties 被定义为字符串列表,LLM 将仅从文本中选择性地检索指定的属性。
llm_transformer_props = LLMGraphTransformer(
llm=llm,
allowed_nodes=["Person", "Country", "Organization"],
allowed_relationships=["NATIONALITY", "LOCATED_IN", "WORKED_AT", "SPOUSE"],
node_properties=["born_year"],
)
graph_documents_props = llm_transformer_props.convert_to_graph_documents(documents)
print(f"Nodes:{graph_documents_props[0].nodes}")
print(f"Relationships:{graph_documents_props[0].relationships}")
Nodes:[Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person', properties={'born_year': '1867'}), Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization')]
Relationships:[Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='Pierre Curie', type='Person'), type='SPOUSE'), Relationship(source=Node(id='Marie Curie', type='Person'), target=Node(id='University Of Paris', type='Organization'), type='WORKED_AT')]
存储到图数据库
生成的图形文档可以使用 add_graph_documents 方法存储到图数据库中。
graph.add_graph_documents(graph_documents_props)